[et_pb_section fb_built=”1″ _builder_version=”4.16″ global_colors_info=”{}”][et_pb_row _builder_version=”4.16″ background_size=”initial” background_position=”top_left” background_repeat=”repeat” global_colors_info=”{}”][et_pb_column type=”4_4″ _builder_version=”4.16″ custom_padding=”|||” global_colors_info=”{}” custom_padding__hover=”|||”][et_pb_text _builder_version=”4.21.2″ background_size=”initial” background_position=”top_left” background_repeat=”repeat” hover_enabled=”0″ global_colors_info=”{}” sticky_enabled=”0″]
“I’d put my money on the sun and solar energy. What a source of power! I hope we don’t have to wait until oil and coal run out before we tackle that.” – Thomas Edison
Thomas Edison’s words from over a century ago are more relevant than ever in today’s world. Solar energy is indeed a powerful source of clean and sustainable energy, and its adoption is growing at an impressive rate. In today’s world, renewable energy sources are becoming increasingly important as we attempt to lower our carbon footprint and reach net zero. Solar energy has emerged as a leading contender among these.
Solar energy systems use the sun’s energy to produce electricity and heat for our homes, businesses, and industries. But did you know that there are numerous types of solar systems? In this blog, we will delve deep to explore the different types of solar energy collectors and their unique characteristics.
3 Types of Solar Power Systems
There are many different types of solar systems; all of them are made to collect solar energy and turn it into electricity that can be used. We’ll examine the different types of solar systems here:
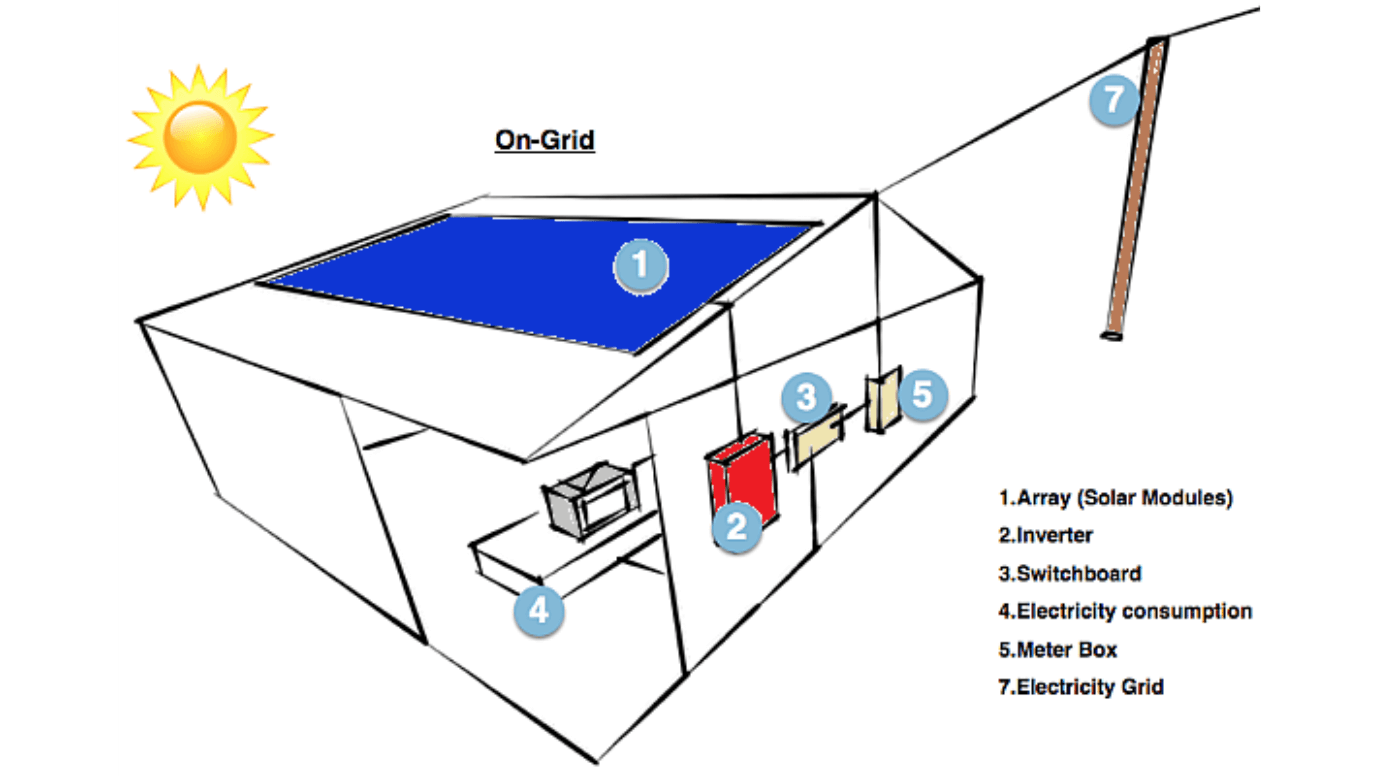
1. On-Grid Solar Power Systems:
Also known as a grid-tie or grid-feed solar system, the most popular type of solar power system for homes and businesses is one that is grid-connected or on-grid. These systems are linked to the public energy grid and run on either microinverters or solar inverters. Homes are usually powered by the solar power that is created, depending on the type of metering in place. Then, the surplus solar energy is exported to the electrical grid, where it is typically compensated for with a feed-in tariff (FiT) or credits.
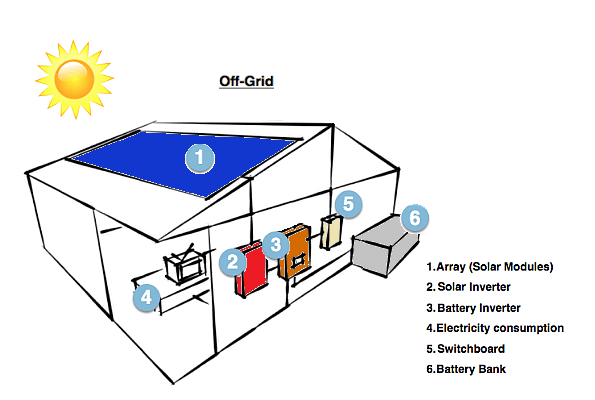
2. Off-Grid Solar Power Systems:
Also known as a stand-alone power system (SAPS), also known as a standalone or independent solar system, is a solar power setup that operates independently of the traditional electrical grid. In other words, it is not connected to a utility’s electrical infrastructure. Off-grid systems are designed to generate and store their own electricity, making them self-reliant and typically suited for locations where grid power is either unavailable or unreliable.
Also Read: What is Solar Energy and How it’s Generated
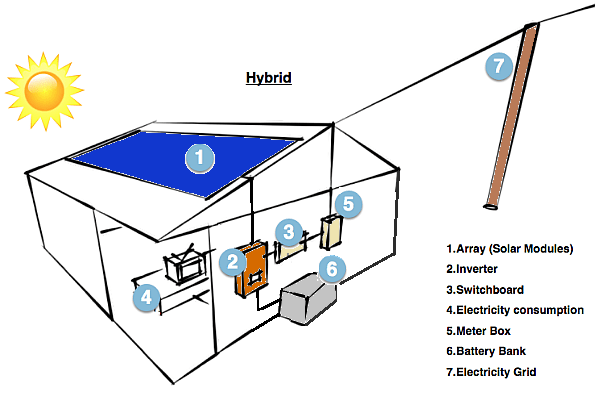
3. Hybrid Solar Power Systems:
A hybrid solar system, often referred to as a solar hybrid system or a hybrid renewable energy system, is a combination of two or more different sources of electricity generation; typically, battery storage is combined. It is then utilized by systems that are already connected to the electrical grid. To do this, solar energy produced during the day must be able to be stored and used at night. Offering customers, the best of both worlds, the grid acts as a backup when the stored energy is used up.
Also Read: What Are the Different Types of Solar Panels?
What Are the Technologies of Solar Power Solutions
There are three major types of solar power systems for generating usable electricity from the sun. For optimal performance, every solar system has a different setup and surface area requirement. Below is a detailed discussion of these systems.
Thermal Solar Power Solutions:
This solar solution uses the sun’s heat to produce electricity. The sun’s rays are partially reflected by several solar collectors. This procedure helps to achieve the high temperatures that are needed to produce consumable electricity. This process produces heat, which raises the fluid’s steam content and drives the turbine to generate power.
Concentrated Solar Power Solutions:
Mirrors, tracking devices, and lenses are used in these solar power systems to focus the sun’s energy. High-intensity solar energy is converted to room temperature with this technology. The engines, or turbines, are then powered by this heat to produce electricity.
Photovoltaic Solar Power Solutions:
Most ground-mounted solar power plants generate solar electricity for commercial purposes. To install solar panels that can collect enough sunlight to produce the necessary amount of electricity for sale, these solar power plants need a sizable amount of land.
Conclusion
Solar energy can readily supply large amounts of low-cost, environmentally friendly electricity. The latest developments in solar power technology are demonstrating the remarkable energy source’s versatility. Furthermore, having different types of solar power systems available makes it easier to generate power efficiently in locations with different power sources. Even though installing solar panels can be expensive, solar systems have many advantages and are the way of the future for electricity generation.
FAQ’s
What are the two main types of solar systems?
There are typically two main types of solar energy systems: photovoltaics (PV) and concentrating solar thermal power (CSP). In a photovoltaic system, when the sun shines on a solar panel, energy from the sunlight is absorbed by the PV cells in the panel. This energy creates electrical charges that move in response to an internal electrical field in the cell, causing electricity to flow.
Whereas, in concentrating solar-thermal power (CSP), the systems use mirrors to reflect and concentrate sunlight onto receivers that collect solar energy and convert it to heat, which can then be used to produce electricity or stored for later use. It is used primarily in very large power plants.
Do solar systems generate electricity on cloudy days?
On cloudy days, solar systems generate power, but at a lower efficiency due to decreased sunlight intensity and scattering. Energy production is affected by factors such as cloud cover thickness and geographical location. Grid connections and energy storage can assist in ensuring a continuous power supply during less productive seasons, such as cloudy days.
[/et_pb_text][/et_pb_column][/et_pb_row][/et_pb_section]