What is solar energy?
Solar energy is one of the most abundant and one of the main types of renewable energy. As we work to reduce pollution and protect our planet, solar power is becoming increasingly important. By using the sun’s energy, we can produce electricity and heat without harming the environment, helping us move towards a more sustainable future.
“I’d put my money on the sun and solar energy. What a source of power! I hope we don’t have to wait until oil and coal run out before we tackle that.” – Thomas Edison
Thanks to advances in technology, solar energy systems are now more efficient and affordable. From photovoltaic technology that turns sunlight into electricity to solar thermal systems that capture the sun’s heat, solar energy is proving to be incredibly versatile and is transforming industries. These systems are not only good for the planet but also create jobs and support the economy.
In this blog, we’ll take a closer look at the different types of solar energy systems.
Read our blog on the What are the advantages of solar energy
What types of solar energy are there?
Solar energy can be captured in different ways, with the two most common types being photovoltaic (PV) and solar thermal energy.
Photovoltaic (PV) Solar Energy:
Photovoltaic solar technology directly converts sunlight into electricity using panels made of semiconductor cells. This process occurs within photovoltaic cells, which are typically made of silicon. When sunlight hits these cells, it excites electrons, causing them to move and generate an electric current. These cells are assembled into panels, which can be used in both small-scale installations, like on rooftops, or in large solar power plants.
PV technology has advanced significantly, with costs decreasing and efficiency increasing over the years. This has led to widespread adoption, supported by government incentives and the ability of solar PV to now compete with traditional electricity sources in many regions. The electricity produced is direct current (DC), which is then converted to alternating current (AC) by an inverter, making it usable for homes, businesses, and even for feeding into the electricity grid.
Check out our blog on the essential checklist for choosing a top solar EPC company.
Solar Thermal Energy
Solar thermal energy harnesses the sun’s heat to generate electricity or provide heating solutions. This process involves using solar collectors, which absorb and store solar radiation. The heat collected is then used to warm water or other fluids, which can support residential, industrial, or hygienic heating systems.
One common method of utilizing solar thermal energy is through solar thermal panels. These panels absorb sunlight and transfer the heat to a working fluid, which can then be used for various purposes such as heating water, warming spaces, or even heating swimming pools. These panels can be either unglazed or glazed, with glazed panels often being more efficient due to their added insulation. This insulation allows the panels to collect heat even on cloudy days, making them effective for low-temperature applications like domestic hot water, space heating, or providing heat for industrial processes.
Recent developments have also explored the use of solar thermal energy to power air conditioning systems, though these applications are still largely experimental.
To explore the various ways solar energy can be used and applied, read our blog on How can solar energy be used and applied
Solar thermal energy provides a versatile and efficient way to harness the sun’s power, offering both heat and electricity for a wide range of applications, from household heating to industrial power generation.
Concentrated Solar Power (CSP)
Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) systems harness the sun’s energy by focusing sunlight using mirrors, lenses, and tracking devices. These systems concentrate sunlight onto a small area, heating a transfer fluid such as oil, gas, or molten salt to very high temperatures. The heated fluid then transfers its energy to a network of water, producing steam that drives turbines to generate electricity.
CSP technology is most effective in regions with intense, direct sunlight, such as deserts, where large power plants can be built. These plants typically cover vast areas with fields of mirrors or curved reflectors that track the sun throughout the day to maximize energy capture. The focused heat from the sun reaches temperatures high enough to create high-pressure steam, which powers turbines connected to electricity generators.
While CSP systems are more complex and costly due to the need for tracking mechanisms and the high temperatures involved, they offer a powerful solution for utility-scale electricity generation in sunny climates.
Concentrated Solar Power is a vital part of the renewable energy landscape, providing a reliable source of electricity in regions with abundant sunlight.
3 Types of Solar Power Systems
There are many different types of solar systems; all of them are made to collect solar energy and turn it into electricity that can be used. We’ll examine the different types of solar systems here:
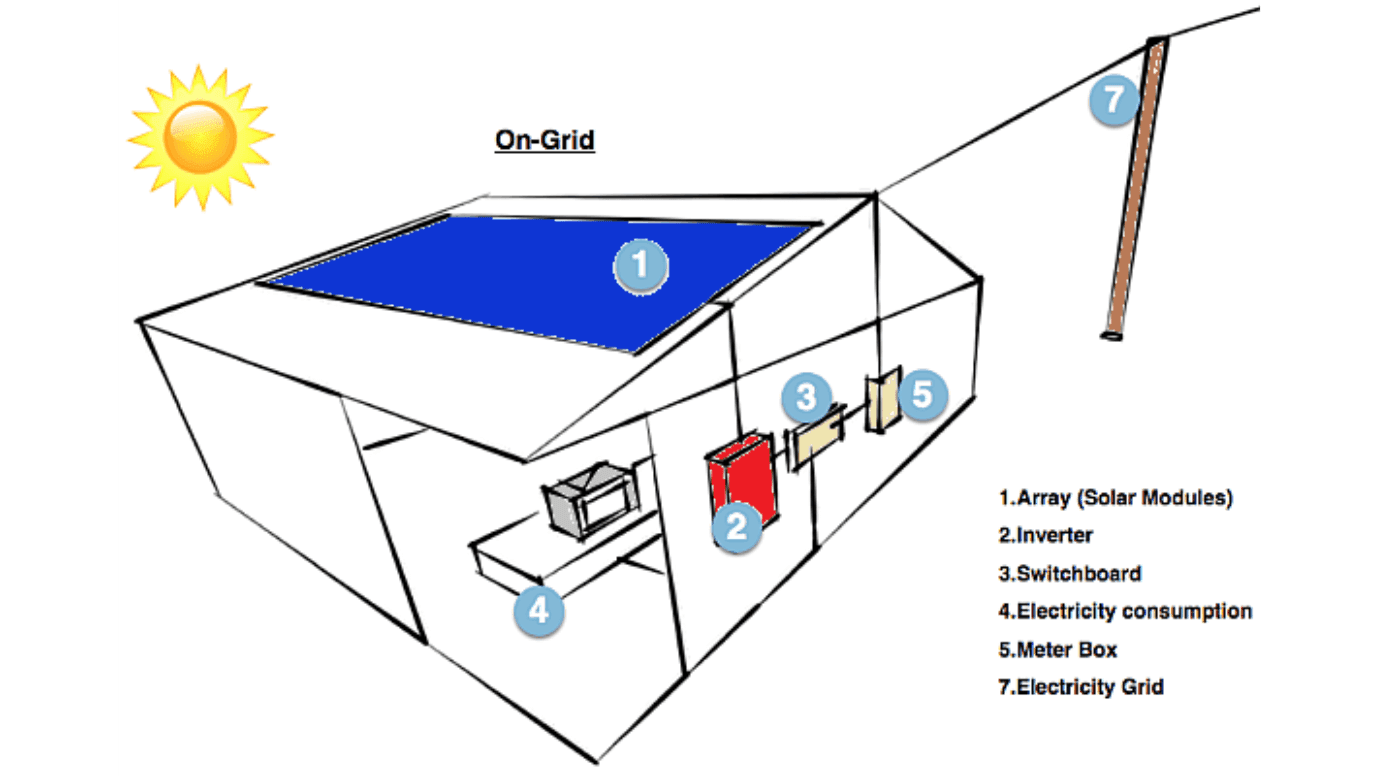
1. On-Grid Solar Power Systems:
Also known as a grid-tie or grid-feed solar system, the most popular type of solar power system for homes and businesses is one that is grid-connected or on-grid. These systems are linked to the public energy grid and run on either microinverters or solar inverters. Homes are usually powered by the solar power that is created, depending on the type of metering in place. Then, the surplus solar energy is exported to the electrical grid, where it is typically compensated for with a feed-in tariff (FiT) or credits.

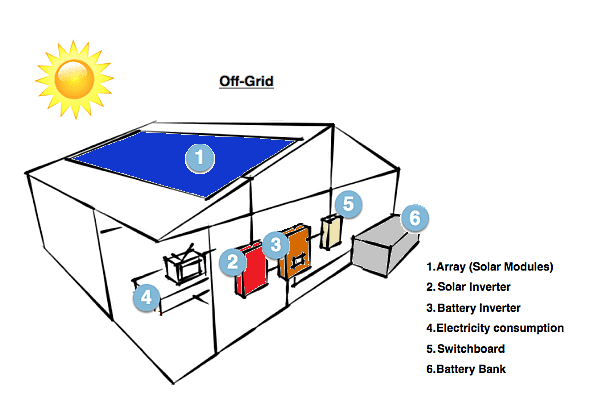
2. Off-Grid Solar Power Systems:
Also known as a stand-alone power system (SAPS), also known as a standalone or independent solar system, is a solar power setup that operates independently of the traditional electrical grid. In other words, it is not connected to a utility’s electrical infrastructure. Off-grid systems are designed to generate and store their own electricity, making them self-reliant and typically suited for locations where grid power is either unavailable or unreliable.
Also Read: What is Solar Energy and How it’s Generated

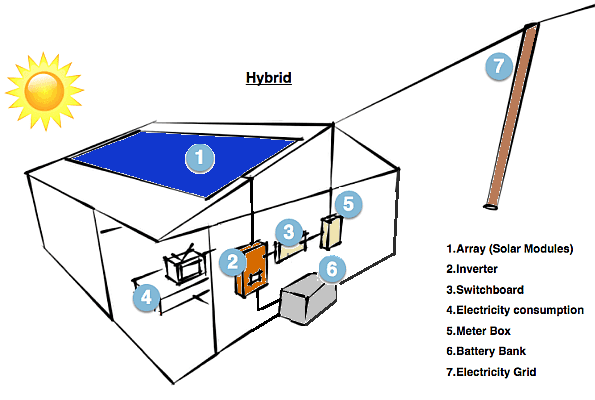
3. Hybrid Solar Power Systems:
A hybrid solar system, often referred to as a solar hybrid system or a hybrid renewable energy system, is a combination of two or more different sources of electricity generation; typically, battery storage is combined. It is then utilized by systems that are already connected to the electrical grid. To do this, solar energy produced during the day must be able to be stored and used at night. Offering customers, the best of both worlds, the grid acts as a backup when the stored energy is used up.

Also Read: What Are the Different Types of Solar Panels?
What Are the Technologies of Solar Power Solutions
There are three major types of solar power systems for generating usable electricity from the sun. For optimal performance, every solar system has a different setup and surface area requirement. Below is a detailed discussion of these systems.
Thermal Solar Power Solutions:
This solar solution uses the sun’s heat to produce electricity. The sun’s rays are partially reflected by several solar collectors. This procedure helps to achieve the high temperatures that are needed to produce consumable electricity. This process produces heat, which raises the fluid’s steam content and drives the turbine to generate power.
Concentrated Solar Power Solutions:
Mirrors, tracking devices, and lenses are used in these solar power systems to focus the sun’s energy. High-intensity solar energy is converted to room temperature with this technology. The engines, or turbines, are then powered by this heat to produce electricity.
Photovoltaic Solar Power Solutions:
Most ground-mounted solar power plants generate solar electricity for commercial purposes. To install solar panels that can collect enough sunlight to produce the necessary amount of electricity for sale, these solar power plants need a sizable amount of land.
Avaada and Solar Energy
At Avaada, our commitment to sustainability and responsibility drives our efforts to meet society’s growing energy demands while reducing carbon emissions. We are dedicated to becoming a leader in renewable energy, with a goal of achieving 30 GW of installed capacity by 2030, supported by a USD 20 billion asset base. This ambitious target will allow us to positively impact the lives of 1 million people.
In line with our mission, we are advancing several key initiatives. We are developing Green Hydrogen and Green Ammonia capacities to support India in its journey to reduce carbon emissions and transition to a greener future. Furthermore, we are establishing a Solar Manufacturing unit to achieve self-sufficiency in the renewable energy sector, reinforcing our commitment to sustainability and energy independence.
Avaada is not just focused on energy generation but also on creating a sustainable and responsible energy ecosystem for the future.
One of our flagship projects is the Bikaner Solar Power Plant in Rajasthan, one of the world’s largest solar power installations. This project underscores our capability to execute large-scale renewable energy projects that contribute to India’s energy security.
Our portfolio of renewable projects also includes large-scale solar power plants and other clean energy solutions designed to create a sustainable and responsible energy ecosystem. Avaada’s focus on innovation and strategic investments in renewable energy underscores a comprehensive approach to building a sustainable future. By integrating advanced technologies, investing in diverse energy solutions, adhering to environmental standards, and engaging with communities, Avaada is contributing significantly to the global transition towards a greener, more sustainable energy landscape.
Conclusion
Solar energy can readily supply large amounts of low-cost, environmentally friendly electricity. The latest developments in solar power technology are demonstrating the remarkable energy source’s versatility. Furthermore, having different types of solar power systems available makes it easier to generate power efficiently in locations with different power sources. Even though installing solar panels can be expensive, solar systems have many advantages and are the way of the future for electricity generation.
FAQ’s
What are the two main types of solar systems?
There are typically two main types of solar energy systems: photovoltaics (PV) and concentrating solar thermal power (CSP). In a photovoltaic system, when the sun shines on a solar panel, energy from the sunlight is absorbed by the PV cells in the panel. This energy creates electrical charges that move in response to an internal electrical field in the cell, causing electricity to flow.
Whereas, in concentrating solar-thermal power (CSP), the systems use mirrors to reflect and concentrate sunlight onto receivers that collect solar energy and convert it to heat, which can then be used to produce electricity or stored for later use. It is used primarily in very large power plants.
Do solar systems generate electricity on cloudy days?
On cloudy days, solar systems generate power, but at a lower efficiency due to decreased sunlight intensity and scattering. Energy production is affected by factors such as cloud cover thickness and geographical location. Grid connections and energy storage can assist in ensuring a continuous power supply during less productive seasons, such as cloudy days.
[/et_pb_text][/et_pb_column][/et_pb_row][/et_pb_section]