Silicon is the dominant material used in solar cells, powering the majority of solar cells and solar panels deployed globally. This element, central to which material is used in solar cell manufacturing, converts sunlight into electricity via the photovoltaic effect. Understanding why silicon is used in solar cells reveals its pivotal role in off-grid solar systems and solar panel installation projects across India.
What Are Silicon Solar Cells?
Silicon solar cells function as semiconductor devices that generate electricity from light. Manufacturers produce them by slicing high-purity silicon ingots into thin wafers, typically 120-140 μm thick. Doping one side with phosphorus on a P-type base, forming a p-n junction essential for electron movement (PERC Technology), while Topcon Solar Cell use an N-type base and Boron doping, making a P-N junction.
When photons strike the silicon cell, they excite electrons, generating a flow of direct current. Anti-reflective coatings and metal contacts optimize light capture and current collection. Commercial silicon solar cells achieve efficiencies of 22-26%, with lab records exceeding 27%. These cells are connected in strings to form silicon solar panels rated from 400W to over 720W.
Monocrystalline silicon solar cells are derived from single-crystal Czochralski method ingots, offering a uniform structure and a higher efficiency of 22–26%. They dominate because silicon’s properties align with practical manufacturing scales and with technological innovations, leading to rapid improvements in efficiency. Single junctions have a high scope of improvements, with theoretical efficiency limits of 29.4%
Why Silicon is Used in Solar Cells
Silicon earns its position due to its 1.12 eV bandgap, perfectly tuned to the solar spectrum’s peak energy. This allows maximum photon absorption while minimizing thermal losses, explaining why silicon is used in solar cell designs over wider-bandgap alternatives. Abundance, as the second-most-common Earth element, ensures supply chain stability, with global production exceeding 500,000 tons annually for photovoltaics.
Thermal stability prevents efficiency drops in hot climates; silicon cells lose only 0.25-0.35% per degree Celsius above 25°C. Unlike organic materials, silicon resists degradation from UV exposure, moisture, and temperature cycles, warranting 25-30-year warranties. Low toxicity avoids environmental hazards associated with cadmium or lead-based cells.
Cost declines driven by economies of scale have brought silicon solar panel prices below ₹20 per watt in India. Refinements like N-type TOPCon technology, used in high-wattage modules, push efficiencies higher while maintaining silicon’s reliability. These factors make silicon the material used in 95% of solar cell production.
Properties Making Silicon Ideal for Solar Applications
Silicon’s indirect bandgap requires thick absorbers, but advanced texturing scatters light for better utilization. A high refractive index demands coatings to reduce reflection losses to below 5%. Passivation layers minimize recombination sites, boosting voltage output.
Mechanical robustness prevents thin wafers from breaking during handling or under hail impacts up to 25mm in diameter. Silicon solar cells can be integrated with bifacial designs, capturing rear-side albedo for 10-30% extra yield. In half-cut configurations, shading losses halve, enhancing partial performance.
Which element is used in solar cell innovation? Silicon enables upgrades to heterojunction (HJT) and TOPCon cells. N-type silicon avoids light-induced degradation, leaving P-type cells behind, which are vital for long-term output.
Silicon vs. Other Solar Materials
Silicon in Off-Grid Solar Systems
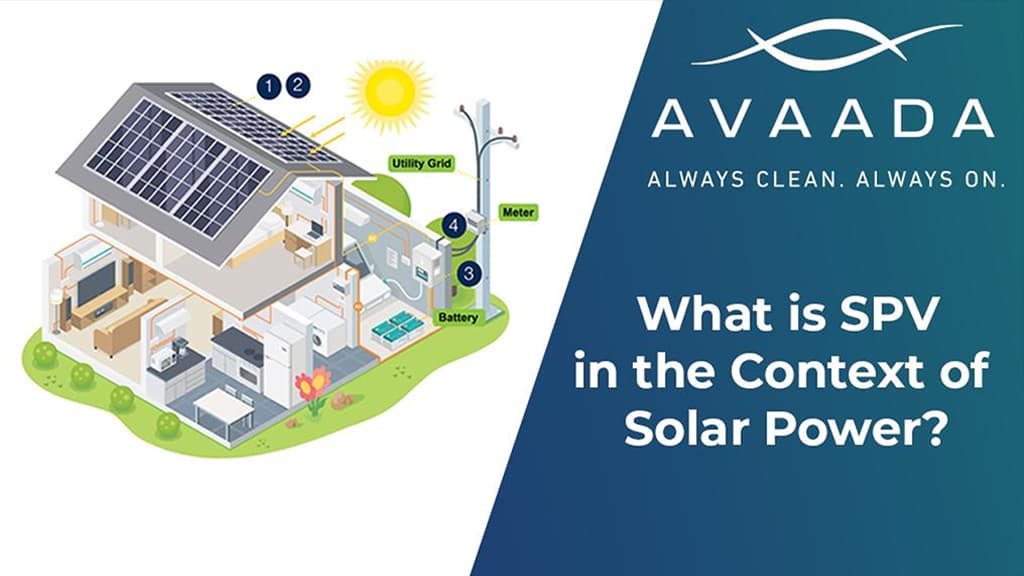
Off-grid solar systems frequently use silicon solar panels to provide reliable power where grid access is unavailable. They power rural water pumps, homes, and telecom towers in states such as Rajasthan and Maharashtra. A typical 5kW system comprises the required number of panels, batteries, and an inverter, supplying around 20-30 kWh daily. Silicon’s stable output better handles variable irradiance than thin films do. Charging controllers prevent battery overcharging, and lithium batteries store solar-generated energy. Some systems include diesel backups for enhanced reliability.
Solar Panel Installation Best Practices
Solar panel installation involves a thorough site survey to assess roof strength, orientation, and shading. In India, optimal tilt angles range from 15 to 30 degrees facing south to maximize annual yield. Ground mounts are preferred for off-grid systems in open areas. Design engineers size panel strings to inverter capabilities, using MC4 connectors for secure electrical connections. Monitoring individual strings ensures performance consistency. Post-installation compliance includes net metering or zero-export devices. Regular cleaning maintains panel output above 98%. India added 26.6 GW solar capacity in early 2025, with ALMM-listed silicon modules required for subsidies.
Future of Silicon Solar Technology
Emerging technologies such as passivated back-contact (IBC) and tandem silicon-perovskite cells aim for efficiencies exceeding 30%. Recycling processes allow recovery of up to 95% silicon, reducing material waste and costs. Integrated plants manufacturing N-type TOPCon modules contribute significantly to India’s self-reliance in solar production. Additionally, 2025 trends show increased adoption of bifacial modules that capture sunlight on both sides, raising energy yields and optimising installation space. The next technology to come is BC (Back Contact) technology, which has the potential to improve the existing Technology by absorbing all the light incident on the front side of the solar cell. Innovations include smart solar panels integrating IoT sensors for real-time performance monitoring and predictive maintenance, boosting system uptime and ROI. Advanced manufacturing techniques, such as low-temperature processing and lower energy consumption during production, make silicon solar cells more sustainable. Research into silicon heterojunctions (HJT) and tandem cells with perovskite layers continues, promising further leaps in efficiency and cost-effectiveness. These developments underscore silicon solar technology’s adaptability and central role in meeting expanding global clean energy demands while supporting India’s solar energy ambitions.
Conclusion
Silicon’s combination of abundance, efficiency, thermal stability, durability, and cost-effectiveness makes it the foremost material for solar cells worldwide. From off-grid applications to large-scale installations, its versatility drives the adoption of clean, sustainable energy. Continuous technological refinements ensure that silicon solar cells will continue to play a pivotal role in powering future renewable energy solutions globally.
Silicon solar panels are preferred in off-grid systems due to their stable output, durability, and consistent performance under varying sunlight conditions. They work efficiently with batteries and inverters, making them ideal for rural homes, pumps, and telecom towers.
FAQs
Why is silicon the most commonly used material in solar cells?
Silicon is widely used in solar cells because it has an ideal bandgap, high efficiency, excellent thermal stability, and long lifespan. Its abundance and low cost make it suitable for large-scale solar panel manufacturing worldwide.
Which element is used in solar cell manufacturing?
Silicon is the primary element used in solar cell manufacturing. It functions as a semiconductor that converts sunlight into electricity through the photovoltaic effect.
What type of silicon is used in solar panels?
Most solar panels use monocrystalline silicon due to its high purity, uniform crystal structure, and superior efficiency compared to other silicon types.
How do silicon solar cells generate electricity?
Silicon solar cells generate electricity when sunlight excites electrons within the silicon wafer, creating an electric current through the p-n junction via the photovoltaic effect.
What is the efficiency of silicon solar cells?
Commercial silicon solar cells achieve efficiencies of 22% to 26%, while advanced technologies such as TOPCon and HJT continue to push efficiency even higher.
Are silicon solar panels suitable for hot climates like India?
Yes, silicon solar panels perform well in hot climates. They exhibit low temperature-related efficiency losses and maintain stable output under high-heat conditions.
What is the lifespan of silicon solar panels?
Silicon solar panels typically last 25 to 30 years and often continue generating power at over 80% efficiency beyond their warranty period.
What is the difference between P-type and N-type silicon solar cells?
P-type cells use boron doping and are more prone to degradation, while N-type silicon cells offer higher efficiency, better performance, and longer operational life.
Why are silicon solar panels preferred for off-grid solar systems?
Silicon solar panels are preferred for off-grid systems due to their reliability, consistent power output, and compatibility with batteries and inverters.
What is the future of silicon solar technology?
The future of silicon solar technology includes TOPCon, heterojunction, back contact (BC), and tandem silicon-perovskite cells, aiming for efficiencies above 30%.