What are Renewable Energy Certificates?
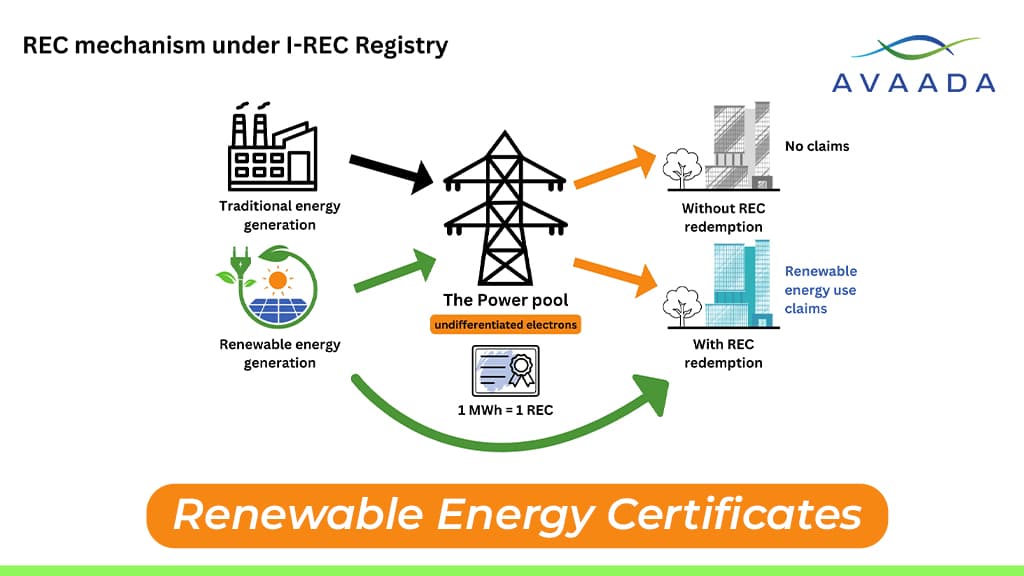
Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs) are market-based instruments that represent the environmental benefits of generating electricity from renewable sources. In simpler terms, one REC is equivalent to one megawatt-hour (MWh) of electricity generated from a renewable energy source such as solar, wind, or hydro. RECs are a critical part of promoting and developing the renewable energy market, allowing companies and organizations to offset their carbon footprint by purchasing certificates without directly generating renewable energy themselves.
To learn more about the advantages of using renewable energy, you can read our blog on the benefits of renewable energy.
Interested in implementing renewable energy solutions? Visit our renewable energy services page to explore how we can help.
How Do Renewable Energy Certificates Work?
RECs serve as a mechanism to support and incentivize the generation of renewable energy. When a renewable energy producer generates electricity, it can sell the physical electricity to the grid while separately selling the environmental attributes (the REC) associated with that electricity.
For instance, a wind farm in India can sell its generated electricity to a utility company while selling the REC to another entity, such as a corporation that wants to claim that it uses renewable energy. The purchase of RECs allows the buyer to claim that their electricity consumption is from renewable sources, even if they are purchasing power from a non-renewable source in practice. This mechanism helps create a market for renewable energy, providing financial returns to renewable energy producers and encouraging further investment in the sector.
To learn more about our achievements, take a look at the list of renewable energy projects completed by Avaada Group.
Why Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs) are Important
RECs play a pivotal role in promoting renewable energy and reducing greenhouse gas emissions. They provide several key benefits:
- Incentivizing Renewable Energy Production: By allowing producers to earn additional revenue through the sale of RECs, these certificates provide a financial incentive to develop new renewable energy projects.
- Supporting Corporate Sustainability Goals: Companies can meet their sustainability targets and reduce their carbon footprint by purchasing RECs, even if they cannot directly source renewable energy for their operations.
- Regulatory Compliance: In India, certain entities are mandated to meet Renewable Purchase Obligations (RPOs), which require them to source a specific percentage of their electricity from renewable sources. RECs provide a flexible and cost-effective way to meet these obligations.
- Driving the Renewable Energy Market: The trading of RECs fosters a competitive market for renewable energy, encouraging investment and innovation in the sector.
To see how sustainability is implemented on a larger scale, explore our sustainability initiatives that contribute to energy and emission management.
How Many Types of RECs are There?
In India, there are two types of RECs:
- Solar RECs: These certificates are issued to renewable energy producers that generate electricity using solar power. Solar RECs typically have higher values due to the relatively higher cost of solar energy generation compared to other renewable sources.
- Non-Solar RECs: Certificates are issued to renewable energy producers that generate electricity from non-solar sources, such as wind, hydro, or biomass. Non-solar RECs tend to have a lower market value compared to solar RECs reflecting the different cost structures of these energy sources.
Who is Eligible for RECs?
Eligibility for RECs in India is determined by several criteria:
- Type of Renewable Energy Source: The electricity must be generated from a renewable source, such as solar, wind, biomass, or hydro.
- Not Tied to Preferential Tariffs: The renewable energy generator must not be selling its electricity under any preferential tariff or power purchase agreement (PPA) with a distribution company. This ensures that RECs are used to support market-driven renewable energy generation.
- Grid-Connected: The renewable energy plant must be connected to the grid, and the electricity generated must be supplied to the grid.
- Compliance with Regulatory Requirements: The renewable energy generator must comply with the regulations set by the Central Electricity Regulatory Commission (CERC) and other relevant authorities.
How Long is a REC Valid?
In India, RECs are valid for 1,095 days (approximately three years) from the date of issuance. This validity period allows the REC holders sufficient time to trade or use the certificates to meet Renewable Purchase Obligations (RPOs) or other sustainability goals. After the expiry of this period, the RECs can no longer be used for compliance or trading purposes.
Who Issues RECs in India?
In India, RECs are issued by the Central Agency, which is appointed by the Central Electricity Regulatory Commission (CERC). The National Load Despatch Centre (NLDC) operates as the Central Agency responsible for issuing RECs to eligible renewable energy generators.
To receive RECs, a renewable energy producer must apply to the Central Agency and meet specific criteria, such as ensuring the renewable energy generated is not tied to any preferential tariffs. Once issued, RECs can be traded on the Indian Energy Exchange (IEX) or the Power Exchange India Limited (PXIL), where obligated entities and voluntary buyers can purchase to meet their Renewable Purchase Obligations (RPOs) or other sustainable goals.
Example: How RECs Work in Practice
Let’s consider a real-world example. Suppose a solar power plant in Rajasthan generates 100 MWh of electricity. The physical electricity is sold to a local utility company that distributes it to consumers. The solar power plant can then receive 100 Solar RECs from the Central Agency (National Load Despatch Centre) as it has produced 100 MWh of renewable energy.
A large corporation in Mumbai, which aims to reduce its carbon footprint and fulfill its Renewable Purchase Obligation (RPO), purchases these 100 Solar RECs from the solar power plant through the Indian Energy Exchange (IEX). By purchasing these RECs, the corporation can claim that 100 MWh of the electricity it consumes is green, even though the physical electricity it uses may come from non-renewable sources.
In addition to generating RECs, renewable energy projects often contribute to larger sustainability goals and infrastructure development. For example, we recently announced plans to build 2,750 MW Pumped Storage Projects in Maharashtra, a significant step towards enhancing renewable energy capacity in India.
For more details, you can read the full press release here.
Conclusion
Renewable Energy Certificates are an essential tool in India’s push towards a greener and more sustainable energy future. By decoupling the environmental attributes from the physical electricity generated, RECs allow for a flexible and market-driven approach to promoting renewable energy. As India continues to strive towards its renewable energy goals, RECs will play a vital role in ensuring that the country meets its environmental and sustainability targets, supporting the growth of the renewable energy sector.