Earth Overshoot Day is the date when humanity’s demand for ecological resources and services in a given year exceeds what Earth can regenerate in that same year. This day, calculated by the Global Footprint Network, serves as a stark reminder of our overconsumption and its impact on the planet. It highlights the ecological deficit created by our current lifestyles, which rely heavily on natural resources.
To learn more about global environmental agreements, you can read our blog on the Kyoto Protocol.
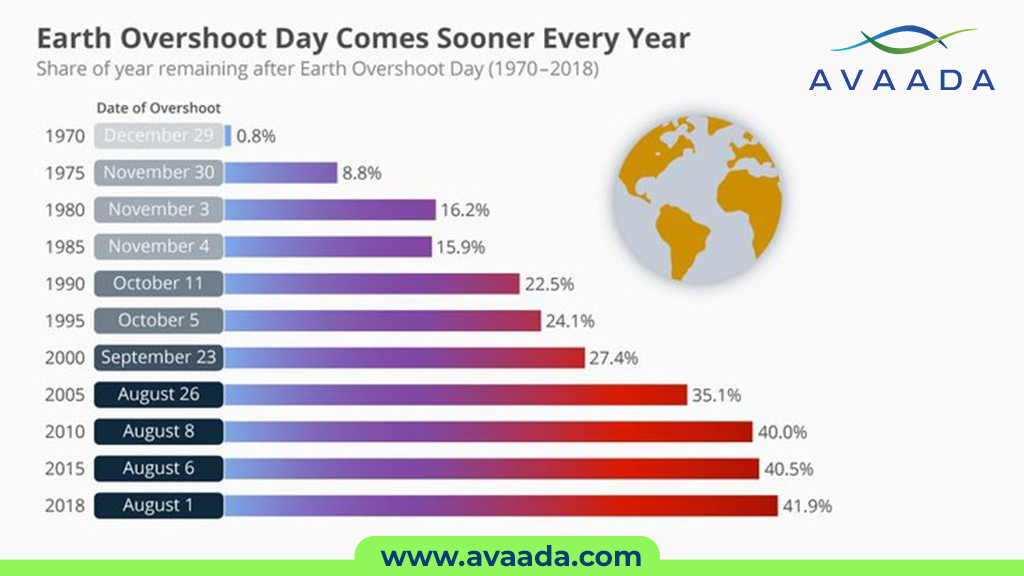
The First Earth Overshoot Day
The concept of Earth Overshoot Day was first introduced in 2006 by the Global Footprint Network. However, the idea of measuring the ecological footprint and biocapacity dates back to the early 1970s.
The first calculated Earth Overshoot Day was December 19, 1987. Since then, the date has been moving earlier in the year, highlighting the increasing rate of resource consumption.
For more insights into how global policies are shaping sustainable practices, explore our post on Net Zero Emissions.
When is Earth Overshoot Day Celebrated in India?
In 2024, Earth Overshoot Day for India was on Thursday, 1st August. This date marks the point in the year when India’s consumption of ecological resources exceeds what the country’s ecosystems can regenerate for that year. Earth Overshoot Day is observed to raise awareness about the need for sustainable practices and ecological balance. Environmental organizations, educational institutions, and concerned citizens often engage in activities such as seminars, tree planting drives, and awareness campaigns on this day.
Discover how renewable energy plays a role in this shift by exploring our Renewable Energy Solutions.
History of Earth Overshoot Day Dates for India
Understanding the progression of Earth Overshoot Day for India helps to illustrate the growing ecological deficit. Here is a look at the history of Earth Overshoot Day for India over the past years:
- 2017: August 2
- 2018: August 1
- 2019: July 29
- 2020: August 22 (due to reduced consumption during the COVID-19 pandemic)
- 2021: July 29
- 2022: July 28
- 2023: July 27
- 2024: August 1
How is Earth Overshoot Day Calculated?
The formula for calculating Earth Overshoot Day (EOD) is as follows:
![]()
Where:
- World Biocapacity represents the planet’s capacity to regenerate resources within a given year.
- World Ecological Footprint measures humanity’s demand for those resources within the same year.
This formula determines the specific date in the year when humanity’s resource consumption surpasses the Earth’s ability to regenerate them.
Example Calculation
If the world’s biocapacity is 12 billion global hectares and the world ecological footprint is 20 billion global hectares, then:
EOD=(20billion global hectares / 12billion global hectares)×365
EOD=(0.6)×365
EOD≈219
So, Earth Overshoot Day would be approximately the 219th day of the year.
By using this formula, researchers can determine the exact date each year when humanity’s consumption exceeds the Earth’s capacity to regenerate resources.
The calculation of Earth Overshoot Day involves the following steps:
- Ecological Footprint Calculation: This measures the demand for resources and services from the environment, including food, fiber, timber, and space for infrastructure, as well as the absorption of carbon dioxide emissions.
- Biocapacity Calculation: This assesses the Earth’s ability to regenerate these resources and absorb waste, considering factors such as arable land, forest areas, pastures, and marine environments.
- Comparison of Demand and Supply: By comparing the ecological footprint with the planet’s biocapacity, researchers determine how much of the Earth’s resources are consumed in a given year.
Earth Overshoot Day for Asian and South Asian Countries
Earth Overshoot Day varies by country based on their specific consumption patterns and ecological footprints. Here are the Earth Overshoot Days for a few selected Asian and South Asian countries in 2024:
- Japan: May 30, 2024
- South Korea: June 5, 2024
- China: June 12, 2024
- Thailand: July 8, 2024
- Malaysia: July 13, 2024
- Indonesia: August 18, 2024
- Philippines: August 24, 2024
- India: August 1, 2024
- Bangladesh: September 18, 2024
- Pakistan: October 5, 2024
- Sri Lanka: October 15, 2024
- Nepal: November 3, 2024
These dates illustrate the wide range of resource consumption habits and their impacts across different nations. Countries with earlier Earth Overshoot Days tend to have higher per capita consumption rates and larger ecological footprints.

The Importance of Earth Overshoot Day
Understanding and observing Earth Overshoot Day is crucial for several reasons:
- Raising Awareness: It highlights the unsustainable nature of current consumption patterns and the need for global cooperation to address environmental challenges.
- Encouraging Action: By recognizing the ecological deficit, individuals, businesses, and governments are motivated to adopt more sustainable practices and policies.
- Promoting Sustainability: The day serves as a platform for promoting renewable energy, conservation efforts, and sustainable resource management.
- Fostering Global Cooperation: Addressing the ecological crisis requires collaboration across borders, with countries learning from each other’s successes and challenges.
Conclusion
Earth Overshoot Day is a powerful tool for raising awareness about the urgent need to adopt sustainable practices and reduce our ecological footprint. By understanding its significance and the calculation behind it, we can better appreciate the importance of balancing our resource consumption with the Earth’s ability to regenerate. Observing Earth Overshoot Day in India and around the world helps drive the message that protecting our planet requires immediate and collective action.
For more ways to engage in sustainable practices, explore our Green Energy Solutions.








